We Use CookiesWe use cookies to enhance the security, performance,
functionality and for analytical and promotional activities. By continuing to browse this site you
are agreeing to our privacy policy
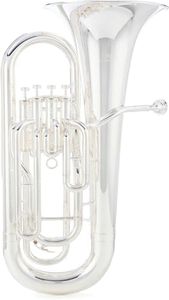
10 Best Euphoniums 2025 in the United States
How do we rank products for you?
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.

FAQ
Most Popular Categories Right Now